Effective Symptom Treatments for Cat Eye Syndrome: A Comprehensive Guide
The rare hereditary condition Cat Eye Syndrome (CES) is caused by aberrant chromosome 22. It influences several physiological systems, resulting in renal problems, heart disorders, and eye abnormalities. Better control of symptoms is essential for improving a patient's quality of life. Early diagnosis facilitates appropriate medical interventions, and the degree of symptoms determines the different treatment choices.
While some people benefit from therapy or medicines, others could require surgery. Monitoring health requires regular visits. Knowing good symptom remedies will enable households to make wise judgments. This guide looks at several approaches for different ailments. It also emphasizes supportive care meant to improve quality of life. Proper management allows patients to lead better lives.
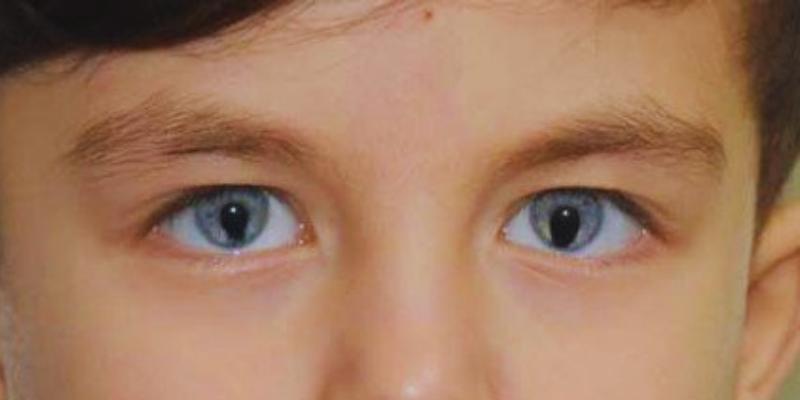
Eye Abnormalities: Treatment and Management
One often-occurring sign of CES is eye problems. Some people have a coloboma disorder, in which ocular tissues are lacking. Thus, vision and ocular performance can be impacted. Frequent eye exams assist in finding early issues. When monitoring eyesight changes, ophthalmologists advise corrective action. Prescription contact lenses or glasses help with minor cases of vision problems. Severe situations could need eye corrections through surgery. Closing eye gaps is one possibility with coloboma surgery.
Laser treatment aids if the retina is damaged. Patients with misaligned eyes could need a strabismus operation. Early treatment improves visual ability and helps to avoid problems. A prevalent problem with CES sufferers is dryness, which is helped by artificial tears. Sunglasses block intense light from damaging delicate eyes. Youngsters should have regular eye tests to monitor their visual development. Parents must do what doctors advise them to to guarantee the greatest results. Some people also find advantages from vision therapy. It increases coordination and tones eye muscles.
Heart Defects: Treatment Approaches
In CES, heart anomalies raise major issues. Congenital cardiac problems run in some patients' families. These disorders may call for surgery and compromise blood flow. Management of cardiac conditions depends on early identification. Echocardiograms let doctors find cardiac problems. Medications aid in blood pressure and cardiac function control. Usually advised are ACE inhibitors or beta-blockers. Severe a cardiac defect calls for surgery.
Open-heart surgery repairs structural defects or holes. Pacemakers help some patients control their heart rate. Lifestyle modifications can help enhance cardiac condition. A balanced diet low in salt reduces blood pressure. Though patients should follow the doctor's advice, exercise helps the heart. Monitoring changes in heart condition depends on regular cardiac tests. A few patients call for lifetime medication. Families should cooperate closely with experts for the best treatment.
Kidney Abnormalities: Management Strategies
Another usual complaint of CES is kidney problems. Certain patients have either underdeveloped or deformed kidneys. These disorders cause either infections or urinary difficulties. Early medical checks guarantee appropriate kidney performance. Ultrasounds let doctors evaluate kidney structure. Blood tests gauge kidney performance. Medications reduce inflammation and infections. Antibiotics cure urinary tract problems. Some individuals need diuretics to stop fluid from building up.
In severe cases, dialysis helps kidneys function. If organs fail, kidney transplants could be required. The health of the kidneys depends on hydration. Every day, patients should sip lots of water. A low-sodium diet lessens kidney workload. Frequent observation helps avoid problems. Families have to teach one another appropriate kidney care. Doctors advise regular visits to track kidney performance over time.

Gastrointestinal Issues: Treatment Options
Many CES patients suffer from digestive system issues; these cover malrotation, constipation, and acid reflux. Appropriate diagnosis guides therapy choice. Doctors use imaging studies to find anomalies. Medications help with symptoms. While antacids ease acid reflux, laxatives help with constipation. Probiotics aid with digestion and gut health. For extreme gastrointestinal problems, some patients need surgery.
Changing diets helps control stomach problems. Foods heavy in fiber help avoid constipation. Regular little meals help lessen reflux problems. Patients should avoid strong and acidic foods. Hydration is vital for digestion. Parents should monitor kids' eating patterns and see a professional. Frequent visits guarantee long-term intestinal health.
Hearing and Speech Therapy for CES Patients
Still another CES symptom is hearing loss. Some are born deaf. Early intervention helps with communication. Doctors evaluate sound perception using hearing exams. In modest conditions, hearing aids improve auditory ability. For extreme hearing loss, one choice is a cochlear implant. Children's language abilities grow with speech treatment. Exercises help therapists to enhance comprehension and pronunciation.
Frequent ear exams help to avoid more problems. Ear infections should be treated as soon as possible. Some patients find great advantages in alternate communication tools like sign language. Expertise helps to increase general communication skills. Families should start early in encouraging speech development.
Developmental Delays and Learning Support
CES can cause developmental delays. Some patients struggle with learning, speaking, and movement skills. Programs aimed at early intervention improve cognitive development. Physical therapy sharpens coordination and movement. Occupational therapy facilitates regular chores. Speech therapy improves the ability to communicate. Programs geared at special education help with learning difficulties.
Teachers provide individualized education based on needs. Development requires patience and encouragement. Parents should partner closely with teachers and therapists. Regular assessments monitor development. Learning benefits from adaptive tools, including assistive technologies. Encouragement of disciplined surroundings helps to improve skills. Regular sessions of therapy improve general development.
Facial and Skeletal Abnormalities: Treatment Plans
Sometimes, CES influences facial form and bones. Certain patients suffer from bone defects or cleft palates. Treatment differs according to degree. Correcting structural problems and cleft palate surgery. Orthodontic procedures straighten teeth. Braces or dental work enhances oral health. Physical therapy increases mobility and tones muscles.
A few patients call for orthopedic treatment. To find anomalies early on, doctors track bone development. Braces, among other supportive tools, help with movement. An appropriate diet supports bone strength. Regular medical visits guarantee long-term gains. Families should follow treatment regimens for the best results.
Conclusion:
Control of Cat Eye Syndrome calls for a multimodal strategy. Crucially important roles are played by renal management, heart monitoring, and eye care. Early diagnosis enhances therapy efficacy. Supportive therapies improve living conditions. Families should consult experts to handle certain issues. Regular medical visits enable one to monitor improvement. Better health results follow from appropriate actions. Customized treatment helps patients to reach better well-being. Families can make wise judgments using awareness and education. Knowing treatments helps one to guarantee the ideal support for their loved ones.












